Brain CT scans are ordered when there a patient suffered serious symptoms in the head area, like severe headaches or dizziness, as well as when a patient suffers an accident with head-related injuries. They are used to diagnose a range of conditions, including aneurysms, bleeding in the brain, strokes, and brain tumors.
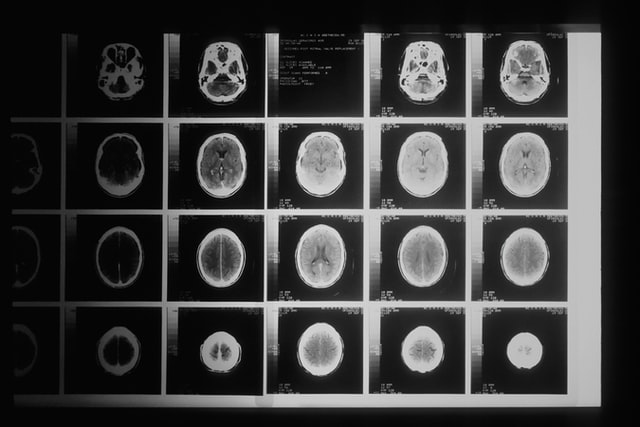
How do brain CT scans work?
Brain CT scans are the same as other types of CT (computed tomography) scans, except they are taken of the head region. They are a diagnostic medical image test that generates multiple images of the skull, brain and blood vessels.
During a brain CT, a donut-shaped device will circle the head and captures pictures of it from various angles. The images that the scan generates are cross-sectional images, which means the images produced are sliced through the middle of the structure. This allows radiologists to clearly see areas that may not be otherwise accessible, and help with a diagnosis.
A brain CT takes a large amount of cross-sectional images. These images can be viewed as flat 2 dimension pictures, or they can be pieced together to make a three-dimensional images. The physician will determine the best method for them to review your results.
Depending on your suspected condition and on the issuing physician, your doctor may order a contrast CT scan. This type of scan involves the patient taking a contrast material, like dye, by mouth or having it injected intravenously. This contrast material can help a physician pick up small abnormalities. A contrast CT scan may require the patient to abstain from food or drink of a certain period of time prior to the scan.
Why might you need a brain CT Scan?
A CT scan is the most common form of brain x-ray ordered. If a doctor or surgeon suspects an injury or issue that’s related to the head or brain area, they will issue one. Brain CT scans are also ordered when a patient has had an injury that is related to the head area.
Brain CT scans are not only used to detect conditions, they can also be used to monitor progress. If a patient is receiving treatment for a brain injury, like radiation for a tumour, a physician may issue a scan to check if the treatment is working effectively.
If you are experiencing any of the following issues, your doctor may order a brain CT scan.
- Seizures
- Persistent, unexplained headaches
- Speech difficulty
- Chronic dizziness
- If a patient has had a stroke
- When structural anomalies are detected
- In the case of an injury, that’s affected the head area
- Vision loss
- Fainting
- If abnormalities are found in a blood or lab test
- To determine the effectiveness of ongoing brain treatment
Below are a number of conditions that a brain CT scan can help diagnose.
- Brain tumours
- Brain aneurysms
- Bleeding of the brain
- Fluid build up in the skull (known as hydrocephalus)
- Brain atrophy
- Structural anomalies
- Brain infection
- Abnormal blood vessels of the brain (known as arteriovenous malformation)
- Other brain conditions
How to prepare for your brain CT Scan
In order to have a brain CT scan, a doctor, surgeon or another medical professional will have to refer you. You should have already discussed your symptoms or problems with the referring physician when they conducted a physical exam.
Preparing for a brain cat scan is very simple and doesn’t require much. In most cases, it’s fine to eat and drink before your appointment. The exception to this is if a contrast scan is being done. If this is the case, and you’re required to avoid food and drink before your appointment, your referring physician will let you know.
To prepare for your appointment you will need to remove all metal objects, like jewelry, piercings, a watch, hairpins and removable hearing aids. If you have a metal object inside your body, like metal plates or screws for an injury or a hearing device that’s surgically implanted, you should let the technician know before the scan.
What to expect from your brain computed tomography scan
During the scan
Upon arrival at the radiology clinic, you will be given a hospital gown to change into for the scan.
You’ll then be asked to lay down on a narrow table, the technician will advise whether they need you lying face up or face down.
Once you’re positioned properly, the scanner table will slowly slide you inside a circular-shaped machine. Brain CT scans are very precise, so it’s important that you hold very still so the image doesn’t get blurred. The technician may ask you to hold your breath for a short period of time.
If the radiologist is conducting a contrast brain CT scan, they will administer contrast material before you enter the cat scan machine. This is usually done intravenously. Sometimes the contrast material will be given as a drink or barium meal. Some patients may experience a slight metal taste from the contrast dye. In very rare cases, the contrast material can cause anaphylaxis for allergic patients, so if you have any trouble breathing at all, you should tell the physician immediately.
If you suffer from claustrophobia you should let your radiologist know. Patients can often feel claustrophobic inside the CT scanner as it is a dark, confined space. If the physician deems it necessary, they will give claustrophobic patients a sedative before the scan.
You’ll be fitted with earphones, to combat the loud noise, and with a buzzer, that will allow you to speak to the technician while inside the CT scanner.
Most brain CT scans take around 30-60 minutes, but this time involves getting ready for the test. The scan itself should only take a few minutes.
Once the scan is completed, the machine will slide the patient back out and you’ll be able to get ready to leave.
After the scan
A head CT scan should be painless and you shouldn’t feel any sensations at all. The only time discomfort or pain may be felt, should be from being uncomfortable on the narrow table or as a result of nervousness from being inside a small space. The scan itself shouldn’t cause any pain or discomfort.
The exception to this is if the scan is being done on an injury. In certain cases, the head will need to be positioned a certain way so that the technician can successfully capture the image they require. In the case of an injury, shifting the head may cause some pain that derives from the injury itself. However, a technician will be very careful when moving you and minimal pain should occur. You should let the doctor know if you feel any.
If you experience any sign of an allergic reaction, like a rash, you should notify a doctor immediately.
Once the scan is finished, you’ll be free to go home and head about your day as usual unless you had a sedative before the scan. In this case, you will need some time to regain full consciousness and should have someone else drive you home. Results are usually ready in around 48 hours after the scan.
What are the benefits of brain CT Scans?
Brain CT scans are an advanced imaging technique that’s used to create detailed pictures of the head area. These images can identify many conditions of the brain. Below are some reasons why CT scans are commonly used.
- They are a non-invasive procedure, meaning minimal pain and they are done quickly and easily without the requirement of a sedative (except in claustrophobic cases).
- They can detect issues that a physical exam can’t confirm such as integrity of brain tissue
- A brain CT scan can image soft tissue, blood vessels and bone all at the same time.
- The results are quick, which can help save the lives of patients in cases that require urgent treatment
FAQs
Why would a doctor order a brain CT Scan?
A doctor will usually conduct a physical exam first. If they are unable to identify the problem or believe that a brain CT scan will help diagnose the condition, they will order one.
How long does a brain CT Scan take?
The actual brain CT scan should only take a few minutes. However, the appointment itself usually takes 30-60 minutes. This includes preparation time, and the time spent speaking with the doctor specially trained to conduct the scan.
Is a brain CT Scan uncomfortable?
A patient shouldn’t experience any sensations from the scan itself. However, they may experience slight side effects if a contrast dye is used. They may also experience discomfort or pain if the scan is conducted for an injury and their technician requires them to be positioned a certain way that affects the injury. In this case, the physician will take utmost care to ensure as little discomfort as possible is caused.


